Semi-Supervised Classification Based on Transformed Learning
-
摘要:
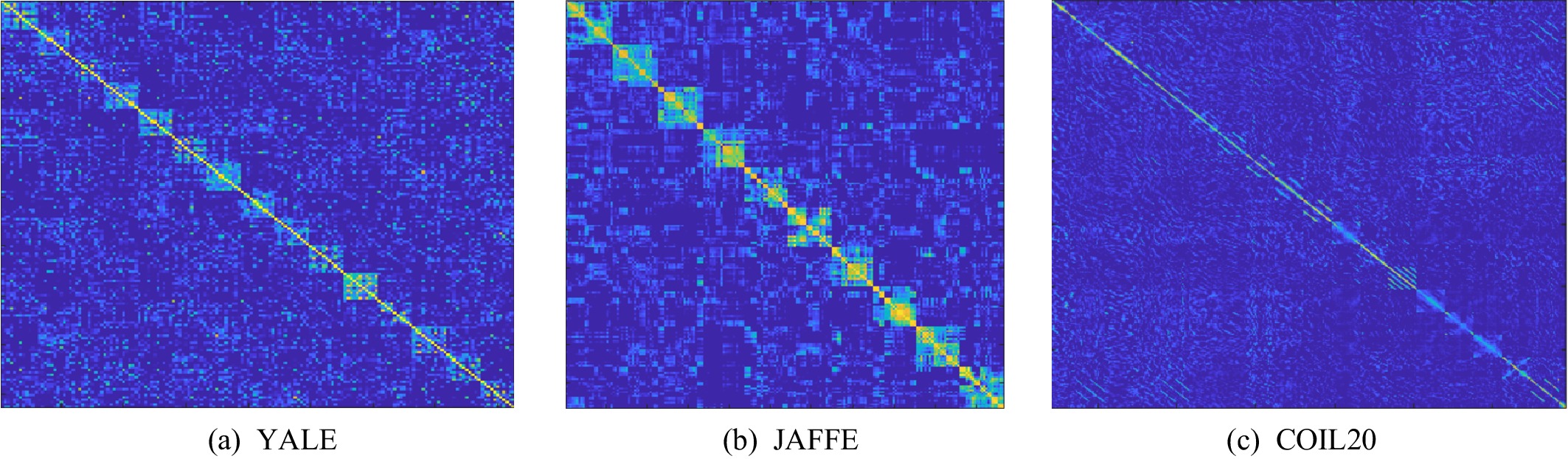
近年来,基于图的半监督分类是机器学习与模式识别领域的研究热点之一. 该类方法一般通过构造图来挖掘数据中隐含的信息,并利用图的结构信息来对无标签样本进行分类,因此半监督分类的效果严重依赖于图的质量,尤其是图的构建方法和数据的质量. 为解决上述问题,提出了一种基于转换学习的半监督分类(semi-supervised classification based on transformed learning, TLSSC)算法.不同于已有的大多数半监督分类算法,此算法试图学习到一个转换空间,并在该空间上构建图,进行标签传播. 具体来说,此算法建立了一个统一的联合优化框架,其由3个部分组成:1)使用转换学习将原始数据映射到转换空间中;2)借鉴数据自表示思想,在转换空间上学习一个图;3)在图上进行标签传播. 这3个步骤交替进行、互相促进,避免低质量图导致的次优解. 对人脸和物品数据集进行实验,结果表明所提出的TLSSC算法在大部分情况下优于现有的其他算法.
Abstract:In recent years graph-based semi-supervised classification is one of the research hot topics in machine learning and pattern recognition. In general, this algorithm discovers the hidden information by constructing a graph and classifies the labels for unlabeled samples based on the structural information of the graph. Therefore, the performance of semi-supervised classification heavily depends on the quality of the graph, especially the graph construction algorithm and the quality of data. In order to solve the above problems, we propose to perform a semi-supervised classification based on transformed learning (TLSSC) in this paper. Unlike most existing semi-supervised classification algorithms that learn the graph using raw features, our algorithm seeks a representation (transformed coefficients) and performs graph learning and label propagation based on the learned representation. In particular, a unified framework that integrates representation learning, graph construction, and label propagation is proposed, so that it is alternately updated and mutually improved and can avoid the sub-optimal solution caused by the low-quality graph. Specially, the raw features are mapped into transformed representation by transformed learning, then learn a high-quality graph by self-expression and achieve classification performance by label propagation. Extensive experiments on face and subject data sets show that our proposed algorithm outperforms other state-of-the-art algorithms in most cases.
-
-
表 1 各种算法在数据集上的Acc实验结果
Table 1 Experimental Results of Classification Accuracy for Each Algorithm on Benchmark Data Sets
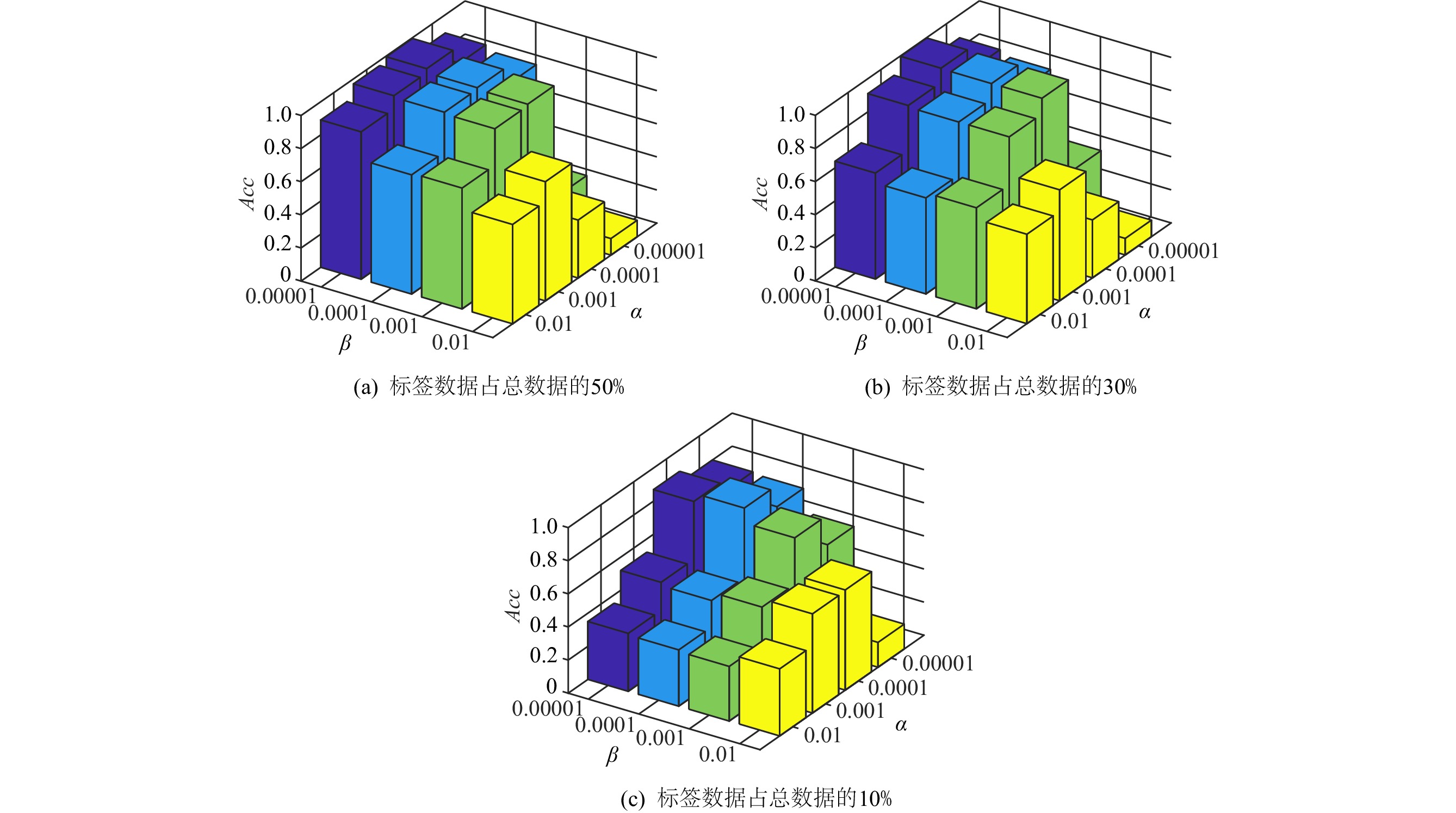
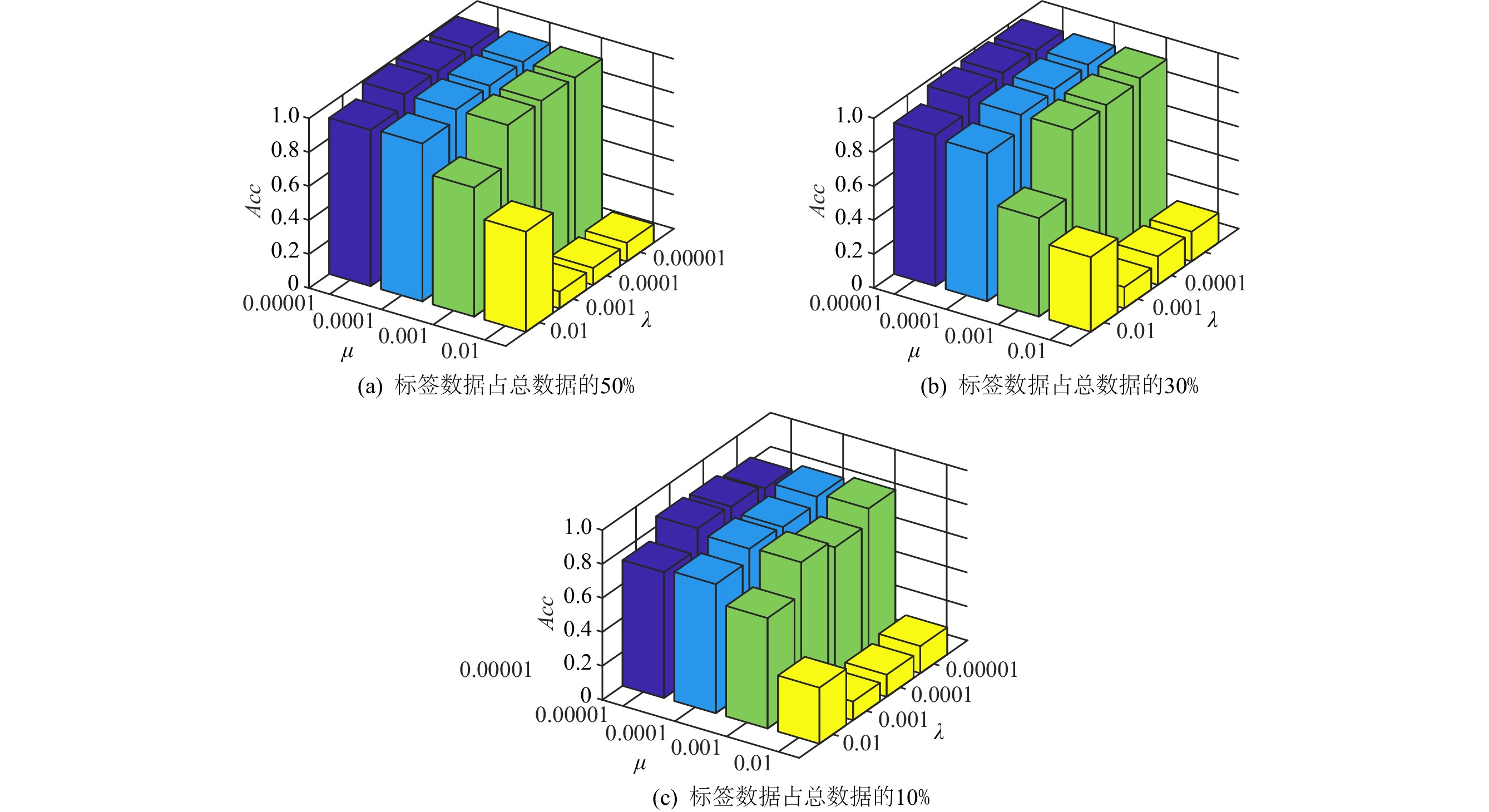
% 数据集 标记数据占比 GFHF LGC SCAN S2LRR TLSSC YALE 10 38.00±11.91 47.33±13.96 45.07±1.30 28.77±9.59 50.00±12.01 30 54.13±9.47 63.08±2.20 60.92±4.03 42.58±5.93 72.88±2.72 50 60.28±5.16 69.56±5.42 68.94±4.57 51.22±6.78 80.11±3.73 JAFFE 10 92.85±7.76 96.68±2.76 96.92±1.68 94.38±6.23 83.83±12.73 30 98.50±1.01 98.86±1.14 98.20±1.22 98.82±1.05 98.98±1.29 50 98.94±1.11 99.29±0.94 99.25±5.79 99.47±0.59 99.51±0.67 COIL20 10 87.74±2.26 85.43±1.40 90.09±1.15 81.10±1.69 87.65±2.0 30 95.48±1.40 87.82±1.03 95.27±0.93 87.69±1.39 96.56±2.04 50 98.62±0.71 88.47±0.45 97.53±0.82 90.92±1.19 97.68±1.69 COIL100 10 51.27±0.73 69.41±1.51 78.95±2.23 44.30±1.56 80.52±2.04 30 64.85±0.49 80.16±1.32 88.39±1.38 58.63±1.44 90.84±1.26 50 72.10±0.70 84.93±1.26 91.98±1.17 62.84±2.49 93.57±1.03 YALEB 10 11.19±1.67 23.76±1.53 55.15±2.49 64.14±3.47 66.83±4.35 30 29.45±2.20 39.69±2.82 69.21±2.55 84.69±0.74 86.91±3.63 50 44.63±1.83 48.74±2.06 73.66±1.80 89.84±0.73 88.59±1.47 注:黑体值为最优结果,±为标准偏差符号. -
[1] 许震,沙朝锋,王晓玲,等. 基于KL距离的非平衡数据半监督学习算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2010,47(1):81−87 Xu Zhen, Sha Chaofeng, Wang Xiaoling, et al. A semi-supervised learning algorithm from imbalanced data based on KL divergence[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2010, 47(1): 81−87 (in Chinese)
[2] 李宇峰,黄圣君,周志华. 一种基于正则化的半监督多标记学习方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2012,49(6):1272−1278 Li Yufeng, Huang Shengjun, Zhou Zhihua. Regularized semi-supervised multi-label learning[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2012, 49(6): 1272−1278 (in Chinese)
[3] 周志华. 基于分歧的半监督学习[J]. 自动化学报,2013,39(11):1871−1878 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01871 Zhou Zhihua. Disagreement-based semi-supervised learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1871−1878 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01871
[4] 张晨光,张燕,张夏欢. 最大规范化依赖性多标记半监督学习方法[J]. 自动化学报,2015,41(9):1577−1588 Zhang Chenguang, Zhang Yan, Zhang Xiahuan. Normalized dependence maximization multi-label semi-supervised learning method[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(9): 1577−1588 (in Chinese)
[5] 陈荣,曹永锋,孙洪. 基于主动学习和半监督学习的多类图像分类[J]. 自动化学报,2011,37(8):954−962 Chen Rong, Cao Yongfeng, Sun Hong. Multi-class image classification with active learning and semi-supervised learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(8): 954−962 (in Chinese)
[6] 张永,陈蓉蓉,张晶. 基于交叉熵的安全Tri-training算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2021,58(1):60−69 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20190838 Zhang Yong, Chen Rongrong, Zhang Jing. Safe Tri-training algorithm based on cross entropy[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(1): 60−69 (in Chinese) doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20190838
[7] 李明,杨艳屏,占惠融. 基于局部聚类与图方法的半监督学习算法[J]. 自动化学报,2010,36(12):1655−1660 Li Ming, Yang Yanping, Zhan Huirong. Semi-supervised learning based on graph and local quick shift[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(12): 1655−1660 (in Chinese)
[8] 张震,汪斌强,李向涛,等. 基于近邻传播学习的半监督流量分类方法[J]. 自动化学报,2013,39(7):1100−1109 Zhang Zhen, Wang Binqiang, Li Xiangtao, et al. Semi-supervised traffic identification based on affinity propagation[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 1100−1109 (in Chinese)
[9] Bo Xiaofan, Kang Zhao, Zhao Zhitong, et al. Latent multi-view semi-supervised classification[C] //Proc of the 11th Asian Conf on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019 [2022-01-27]. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v101/bo19a.html
[10] Kang Zhao, Pan Haiqi, Hoi S C H, et al. Robust graph learning from noisy data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(5): 1833−1843 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2887094
[11] Kang Zhao, Xu Zenglin, Lu Xiao, et al. Self-weighted multiple kernel learning for graph-based clustering and semi-supervised classification[C] //Proc of the 27th Int Joint Conf on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press, 2018: 2312−2318
[12] 刘钰峰,李仁发. 异构信息网络上基于图正则化的半监督学习[J]. 计算机研究与发展,2015,52(3):606−613 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20131147 Liu Yufeng, Li Renfa. Graph regularized semi-supervised learning on heterogeneous information networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(3): 606−613 (in Chinese) doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20131147
[13] Zhu Xiaojin, Ghahramani Z. Learning from labeled and unlabeled data with label propagation, CMU-CALD-02-107[R]. Pittsburgh, PA: Carnegie Mellon University, 2002
[14] Jebara T, Wang Jun, Chang Shifu. Graph construction and b-matching for semi-supervised learning[C] //Proc of the 26th Annual Int Conf on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2009: 441−448
[15] Cheng Hong, Liu Zicheng, Yang Jie. Sparsity induced similarity measure for label propagation[C] //Proc of the 12th Int Conf on Computer Vision. Los Alamitos, CA: IEEE Computer Society, 2009: 317−324
[16] Li Sheng, Fu Yun. Learning balanced and unbalanced graphs via low-rank coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 27(5): 1274−1287
[17] Wang Fei, Zhang Changshui. Label propagation through linear neighborhoods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 20(1): 55−67
[18] Nie Feiping, Cai Guohao, Li Xuelong. Multi-view clustering and semi-supervised classification with adaptive neighbours[C] //Proc of the 31st AAAI Conf on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press, 2017: 2408−2414
[19] Kang Zhao, Guo Zipeng, Huang Shudong, et al. Multiple partitions aligned clustering[C] //Proc of the 28th Int Joint Conf on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press, 2019: 2701−2707
[20] Maggu J, Majumdar A, Chouzenoux E. Transformed subspace clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2020, 33(4): 1796−1801
[21] Ravishankar S, Bresler Y. Learning sparsifying transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 61(5): 1072−1086
[22] Ravishankar S, Wen B, Bresler Y. Online sparsifying transform learning—part I: Algorithms[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(4): 625−636 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2417131
[23] Ravishankar S, Bresler Y. Online sparsifying transform learning—part II: Convergence analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(4): 637−646 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2407860
[24] Zhu Xiaojin, Ghahramani Z, Lafferty J D. Semi-supervised learning using Gaussian fields and harmonic functions[C] //Proc of the 20th Int Conf on Machine Learning. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press, 2003: 912−919
[25] Nie Feiping, Wang Hua, Huang Heng, et al. Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning via ℓ1-norm graph [C] //Proc of the 13th IEEE Int Conf on Computer Vision. Los Alamitos, CA: IEEE Computer Society, 2011: 2268−2273
[26] 古楠楠,樊明宇,王迪,等. 基于仿射子空间稀疏表示的半监督分类[J]. 中国科学:信息科学,2015,45(8):985−1000 doi: 10.1360/N112015-00106 Gu Nannan, Fan Mingyu, Wang Di, et al. Semi-supervised classification based on affine subspace sparse representation[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2015, 45(8): 985−1000 (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N112015-00106
[27] Lu Canyi, Min Hai, Zhao Zhongqiu, et al. Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression [C] //Proc of the 12th European Conf on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 347−360
[28] Mohar B, Alavi Y, Chartrand G, et al. The Laplacian spectrum of graphs[J]. Graph Theory, Combinatorics, and Applications, 1991, 2(12): 871−898
[29] Chung F R K. Spectral Graph Theory[M]. Providence, Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society, 1997
[30] Zhou Dengyong, Bousquet O, Lal T N, et al. Learning with local and global consistency[C] //Proc of the 16th Int Conf on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2003: 321−328
[31] Li Chunguang, Lin Zhouchen, Zhang Honggang, et al. Learning semi-supervised representation towards a unified optimization framework for semi-supervised learning[C] //Proc of the 15th IEEE Int Conf on Computer Vision. Los Alamitos, CA: IEEE Computer Society, 2015: 2767−2775





 下载:
下载: